Introduction
Welcome to our study plan for English Grammar, designed for those preparing for the IELTS ("IELTSExam") or ESL. This guide is also perfect for anyone who wants to improve their English language skills.
English Grammar is a fundamental aspect of language learning, and having a solid understanding of its rules and principles can greatly improve your ability to communicate effectively.
In this study plan, we will provide you with a roadmap to mastering English Grammar, covering the key areas that you need to focus on to achieve success. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced learner, this guide will help you build a strong foundation in English Grammar and take your language skills to the next level.
Watch a quick video introduction:
1. Introduction to Grammar
-
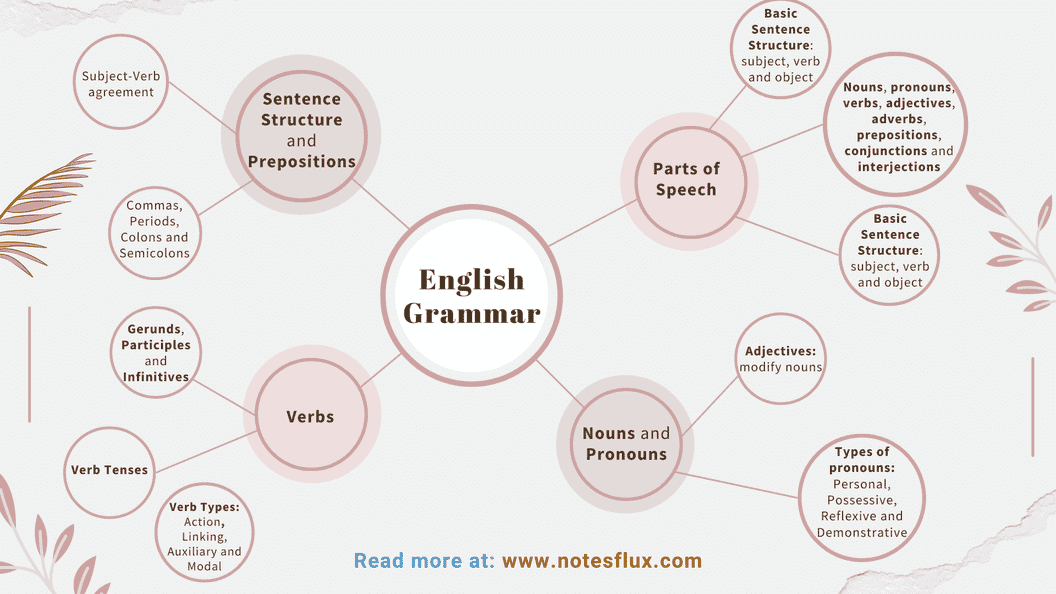
Parts of speech: Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections
-
Basic sentence structure: Subject, verb, object
-
Types of sentences: Simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences
In English grammar, understanding the structure of simple sentences is very important. These sentences comprise three essential components: the subject (who or what the sentence is about), the verb (expressing the action or state), and the object (the entity receiving the action). Together, they construct the foundation of coherent communication.
2. Nouns and Pronouns
-
Common nouns vs. proper nouns
Common nouns, like "teacher" or "city," refer to general people, places, or things. They are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
In contrast, proper nouns, such as "Mr. Smith" or "Sydney," are specific and unique. They always start with capital letters.
Common nouns are used broadly, while proper nouns specify particular entities. Understanding this difference helps in constructing clear and meaningful sentences. For example, "Mr. Smith (proper noun) is our English teacher (common noun)." Both types of nouns play essential roles in effective communication and writing.
Countable and uncountable nouns
Pronouns: Personal, possessive, reflexive, and demonstrative
Take a Grammar Quiz:
3. Verbs
-
Types of verbs: Action, linking, and auxiliary
-
Verb tense: Present, past, and future
-
Regular and irregular verbs
-
Modal verbs: Can, could, may, might, should, shall, will, and would
Modal verbs are special helper words in English grammar, such as "can", "must", and "should". Think of modal verbs as tools that help us express things like ability (what we can do), necessity (what we must do), and permission (what we're allowed to do). For example, "I can swim" shows ability, while "You must study" talks about necessity.
Modal verbs make our sentences more precise and polite. They're important in conversations and writing to convey the right tone and meaning. So, next time you want to say something specific, think about using these helpful modal verbs.
4. Adjectives and Adverbs
Descriptive adjectives
Comparative and superlative adjectives
Adverbs of time, place, and manner
5. Prepositions and Conjunctions
Common prepositions: In, on, at, to, with, for, from
Coordinating conjunctions: And, but, or, so, yet
-
Subordinating conjunctions: Although, because, if, since, when, while
Take a Grammar quiz:
6. Sentence Structure and Punctuation
Subject-verb agreement
Direct and indirect objects
Run-on sentences and sentence fragments
Commas, periods, colons, and semicolons
7. Common Errors to Avoid
-
Confusing similar words: Their/there/they're, or your/you're. Learn more about homophones.
Misusing articles: "A", "an", and "the"
-
Commonly misused verbs: Lie vs. lay, sit vs. set, rise vs. raise
8. Review and Practice
Exercises and quizzes to reinforce learning
-
Try rewriting or expressing a given piece of information using your own words. For this, you can choose a news report about something you like or rephrase the latest news that catches your attention.
English Grammar Mind-Map:




 Subject-Verb Agreement Quiz
Subject-Verb Agreement Quiz